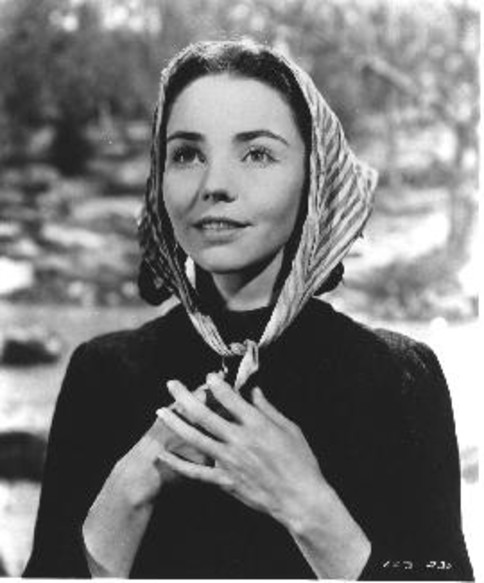
Jennifer Jones in ‘The Song of Bernadette’ (1943)
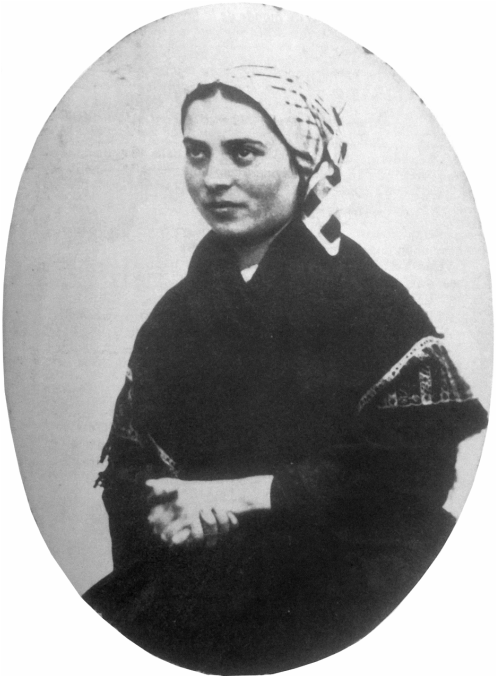
Today is the feast day of Saint Bernadette Soubirous, whose name is inseparable from Lourdes, the French town in which she claimed to have seen a series of apparitions of the Virgin Mary in 1858. Almost immediately, crowds of the devout and the curious began assembling at the spot in the hope of seeing something themselves, and after Bernadette unearthed a hidden spring, it was not long before the healing waters of Lourdes became an international site of pilgrimage. She herself left Lourdes and became a nun, joining the community of the Sisters of Charity of Nevers hundreds of miles to the north. As Sister Marie-Bernarde, she died at the convent of Saint Gildard in Nevers on this day in 1879, aged only 35.
Bernadette’s story has inspired countless books and works of art but today I wanted to write a short post about the film The Song of Bernadette (Henry King, 1943), starring Jennifer Jones as the young visionary.
The film was based on a book, Das Lied von Bernadette, by Franz Werfel (1890-1945), an Austrian Jew who had taken refuge in Lourdes for several weeks while fleeing from the Nazis in 1940. During his time there he heard firsthand tales of the apparitions from older inhabitants of the town, and determined to write about Bernadette if he escaped. True to his word, he completed the novel not long after he and his wife found safety in America. The book was published in German in 1941 (the title page of the first edition is dated Los Angeles, May 1941), followed by an English edition – translated by Ludwig Lewisohn – the following year. It was enormously popular, topping the New York Times bestseller list for weeks on end, and Hollywood producers were not slow to see the potential. The rights were snapped up by 20th Century Fox and workmen began constructing a mock French village on the back lot of the studio. Filming began in March 1943.
Given the popularity of the book, there was intense anticipation as to who would play the part of Bernadette. Gene Tierney, Anne Baxter and Linda Darnell were among those who did screen tests, but the coveted role was given to newcomer Jennifer Jones, whose only screen performances to date had been minor parts in the John Wayne western New Frontier (George Sherman, 1939) and the serial Dick Tracy’s G-Men (John English & William Whitney.1939), both under her real name of Phyllis Isley. At the age of 24 and possessing a youthful fresh-faced beauty, she gave a convincing performance in portraying the fourteen year old Bernadette.
The Virgin Mary was played by Linda Darnell, soon to appear in the racy Forever Amber, and at that time engaged in a scandalous affair with 20th Century Fox boss Darryl F Zanuck.

Linda Darnell as the Virgin Mary
Sadly, Jones’s married life was far from happy at this time. While still in her teens in 1939 she had married actor Robert Walker, with whom she had two young sons. Both actors were struggling until they came to the attention of MGM producer David Selznick, who gave Walker a contract, changed his wife’s name to Jennifer Jones and set her on a course for movie stardom. His plans for her were not disinterested, however, and their affair led to her separation from Walker in November 1943, a few weeks before Song of Bernadette was released in time for Christmas.
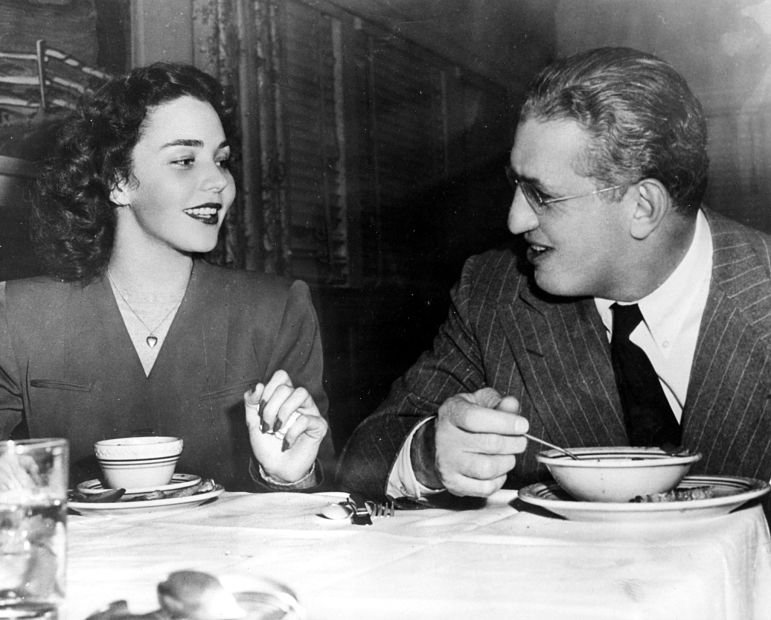

Jones and Selznick
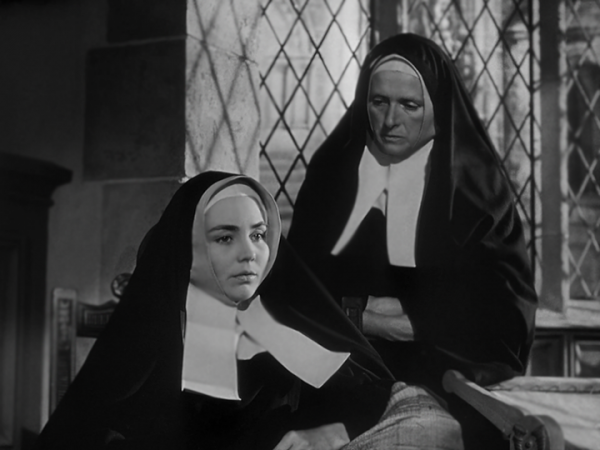

Srs. Marie-Bernarde (Jones) and Marie-Therese (Gladys Cooper) in a poignant scene
On 2 March 1944, her 25th birthday, Jones was awarded an Oscar for her performance, winning out against Ingrid Bergman in
For Whom the Bell Tolls. The Swedish actress was gracious in defeat, and the following year Jones was able to hand Bergman the Oscar for Best Actress in honour of her role in
Gaslight (1944)
, MGM’s remake of the
Anton Walbrook masterpiece of 1940.

Jennifer with her 1944 Oscar – her only one, despite being nominated on four subsequent occasions
Jennifer’s Oscar should not eclipse excellent performances given by other members of the cast, such as Gladys Cooper as Sister Marie-Therese Vazous and Vincent Price (below) as Prosecutor Vital Dutour, whose hostility towards Bernadette’s piety drives him to interrogate her without mercy in the hope of revealing her to be a fraud – although he is nowhere near as cruel an Inquisitor as Matthew Hopkins, whom Price would play in Witchfinder General (Michael Reeves, 1968.)
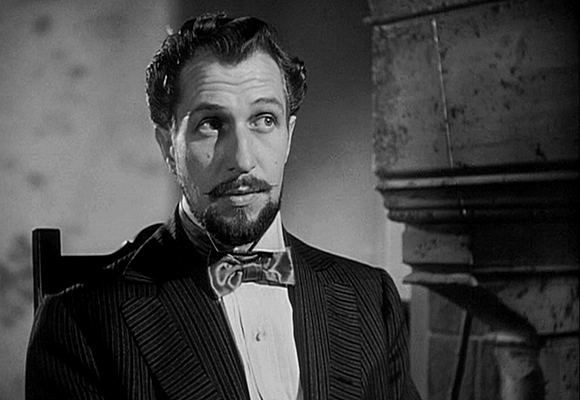

Vincent Price as Vital Dutour
In reality, Dutour was as much a Catholic as Bernadette, and the portrayal of Dutour as irreligious is just on example of the way that the film follows Werfel’s fictional embellishments. The novel is a thick tome of almost 600 pages, and the author used the story to explore related themes about religious experience, attitudes to the supernatural and the nature of miracles, weaving these into a multi-layered narratives of events that took place at the shrine long after the apparitions. One of the film’s flaws is the inclusion of too much of this material, which slows the pace and drags its length out to almost two and a half hours.
Other characters include the parish priest of Lourdes, Abbé Dominique Peyramale, played by Christopher Bickson who would reprise the role in a 1954 radio version. Bickson’s untimely death in 1967 so distressed Jennifer Jones that she attempted suicide. Selznick, whom she had married in 1949, had died in 1965 and their daughter Mary committed suicide in 1976. The third act of The Song of Bernadette depicts the saint’s suffering under humiliation and terminal illness, exploring the possibility that her trials may have been redemptive in nature; one can only wonder if the actress found any such meaning in the troubled years of her later life. Lee J. Cobb (Doctor Dozous) is perhaps better known now for his role as Lieutenant Kinderman in The Exorcist (William Friedkin, 1971), which is one of the very few other Hollywood movies to take the supernatural aspects of religion seriously.
The subtle, almost understated handling of religion in The Song of Bernadette works in the film’s favour, keeping the human drama to the fore; it would have been so easy to sink on the one hand into saccharine sentimentality and on the other into strident piety repellent to a large part of the potential audience. Jennifer Jones’s performance brought out the elements of innocent dignity and strong-willed simplicity Bernadette’s contemporaries saw in the girl, although it is another weakness of the film that the more complex and ambiguous elements of her story are omitted. Those who wish to learn more about the discordant notes in ‘the song of Bernadette’ might like to read Ruth Harris, Lourdes: Body and Spirit in a Secular Age (Allen Lane, 1999) or Therese Taylor, Bernadette of Lourdes: Her life, death and visions (Burnes & Oates, 2006.)